New Publications for PACE Lab Students!
Two new articles co-authored by PACE Lab members were published online in August. Chantal LaFlamme, an current senior at UGA, co-authored a systematic literature review on the associations between stair use and mental health. Former PACE Lab doctoral student, Dr. Erika Rees-Punia, assisted with the analyses assessing the role of intervention implementation on fruit and vegetable consumption among children living in residential children’s homes. This study is part of the Environmental Interventions in Residential Children’s Homes (ENRICH) project led by Drs. Ruth Saunders (University of South Carolina) and Alexandra van den Berg (UT Health). Great work!

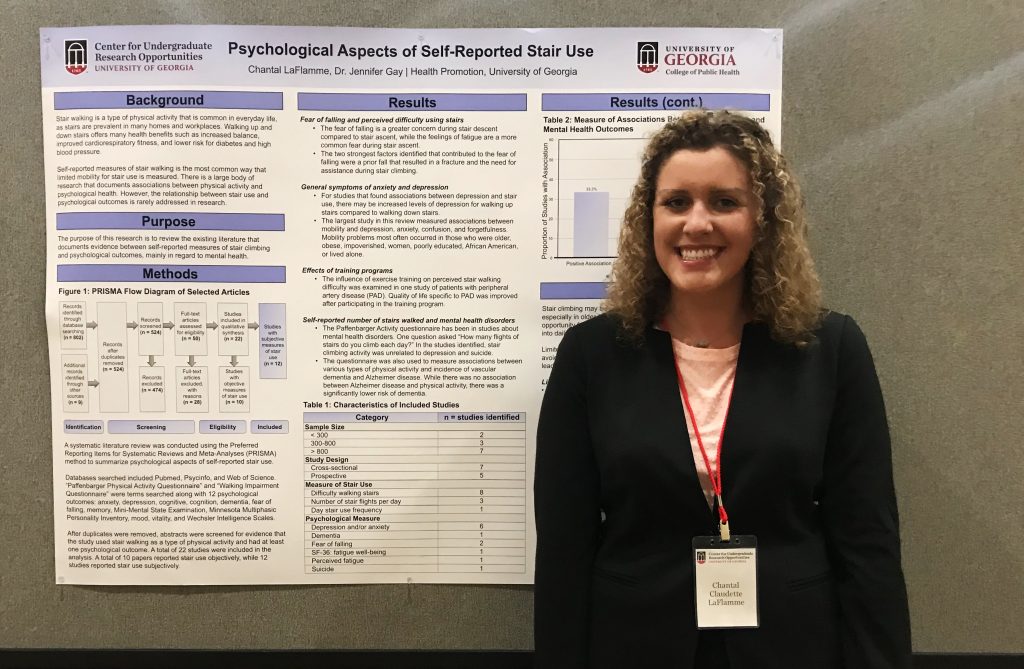
Stair use, a common lifestyle activity, is a moderate-to-vigorous physical activity that, despite often being brief in duration, may contribute to psychological health. A systematic literature review was conducted using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) method to summarize psychological aspects related to stair use. Included studies examined at least one psychological outcome in relation to either objective measures of stair use such as time or stair height, or subjective measures of, or related to, stair use such as perceived difficulty using stairs. A total of 22 studies met the inclusion criteria, 12 used subjective stair use measures and 10 used objective stair use measures. The limited evidence from studies using self-reports supported that (i) perceived difficulty using stairs was positively associated with increased symptoms of anxiety and depression, and (ii) stair use was not associated with a reduced incidence of mental illnesses such as depression, suicide or dementia. Studies using objective measures of stair use supported that (iii) elevated symptoms of anxiety and depression are negatively associated with stair use performance. Given the widespread use of stairs there is surprisingly little data about the extent to which, and for whom, stair use influences psychological health.
PACE Lab Teams Up, Awarded Presidential Interdisciplinary Seed Grant
Dr. Jennifer Gay is part of a team, led by Economic Evaluation Research Group Director, Dr. Janani Thapa, to assess the impact of food and activity environments on Georgia SHAPE Policy outcomes. The team includes researchers from the College of Public Health, Franklin College of Arts and Sciences, College of Education, and College of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences. In addition to publishing the findings, the team’s goal is to use results from this study to support additional future funding. https://news.uga.edu/new-interdisciplinary-seed-grants-2019/
PACE Lab Publishes New Research!
Congratulations to Anita Reina and Marcus Dumas, doctoral students in the PACE Lab, for publishing a first-authored paper, Body image and weight management among Hispanic American adolescents: Differences by sport type in the Journal of Adolescence!


Dr. Jennifer Gay featured in UGA’s Public Service & Outreach News
Dr. Jennifer Gay’s collaborative project with UGA Marine Extension and Georgia Sea Grant on active volunteering is featured in the latest news from the Public Service & Outreach office. Read the story here.
PACE Lab Graduate, Dr. Erika Rees-Punia, Publishes New Research

Congratulations to Dr. Rees-Punia, now a post-doctoral fellow at the American Cancer Society, for publishing part of her dissertation research. Here is the abstract from her recent publication:
Introduction
Excess sitting is a risk factor for early mortality. This may be resulting, at least in part, from the displacement of physical activity with sedentary behaviors. The purpose of this observational study was to examine the mortality risk reductions associated with replacing 30minutes/day sitting for an equivalent duration of light or moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA).
Methods
Participants included 37,924 men and 54,617 women in the Cancer Prevention Study-II Nutrition Cohort, of which 14,415 men and 13,358 women died during follow-up (1999–2014). An isotemporal substitution approach to the Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to estimate adjusted hazard ratios and 95% CIs for mortality associated with the substitution of 30minutes/day self-reported sitting for light physical activity or MVPA. Analyses were conducted in 2018.
Results
Among the least active participants (≤17minutes/day MVPA), the replacement of 30minutes/day sitting with light physical activity was associated with a 14% mortality risk reduction (hazard ratio=0.86, 95% CI=0.81, 0.89) and replacement with MVPA was associated with a 45% mortality risk reduction (hazard ratio=0.55, 95% CI=0.47, 0.62). Similar associations were seen among moderately active participants (light physical activity replacement, hazard ratio=0.94, 95% CI=0.91, 0.97; MVPA replacement, hazard ratio=0.83, 95% CI=0.76, 0.88). However, for the most active (MVPA >38 minutes/day), substitution of sitting time with light physical activity or MVPA was not associated with a reduction in mortality risk (hazard ratio=1.00, 95% CI=0.97, 1.03, and hazard ratio=0.99, 95% CI=0.95, 1.02, respectively).
Conclusions
These findings suggest that the replacement of modest amounts of sitting time with even light physical activity may have the potential to reduce the risk of premature death among less active adults.
Three PACE Lab Students Present Their Research
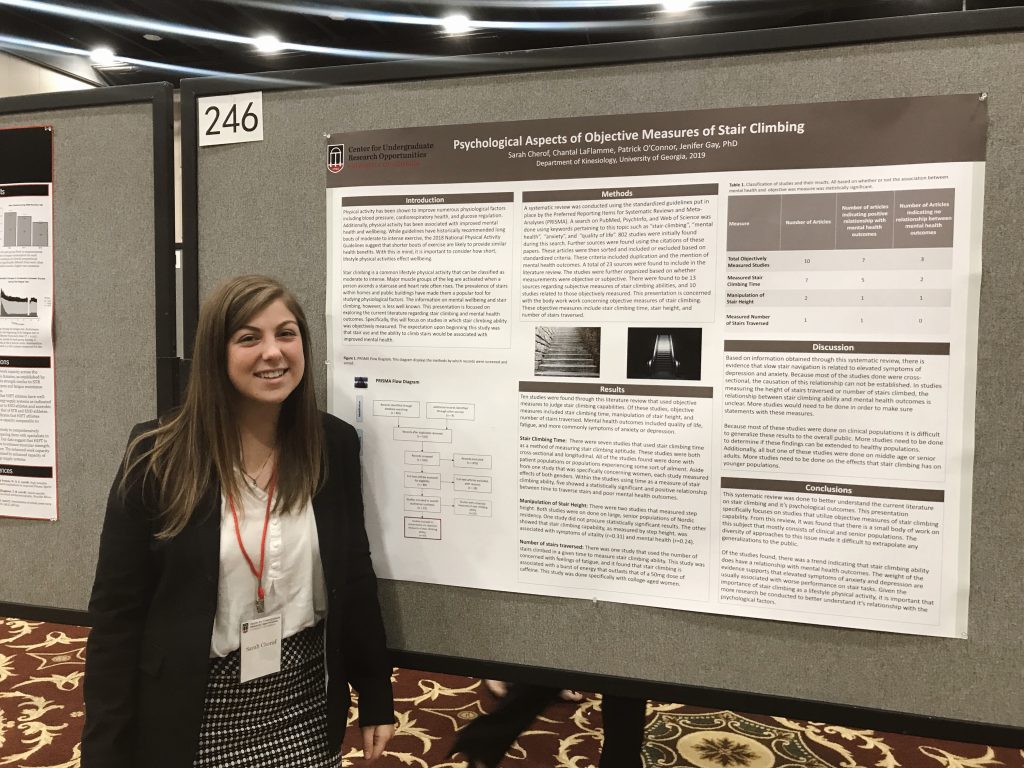
Catriona Geddes, Chantal LaFlamme, and Sarah Cherof presented the results of their research projects at the Center for Undergraduate Research Opportunities (CURO) annual symposium this week.
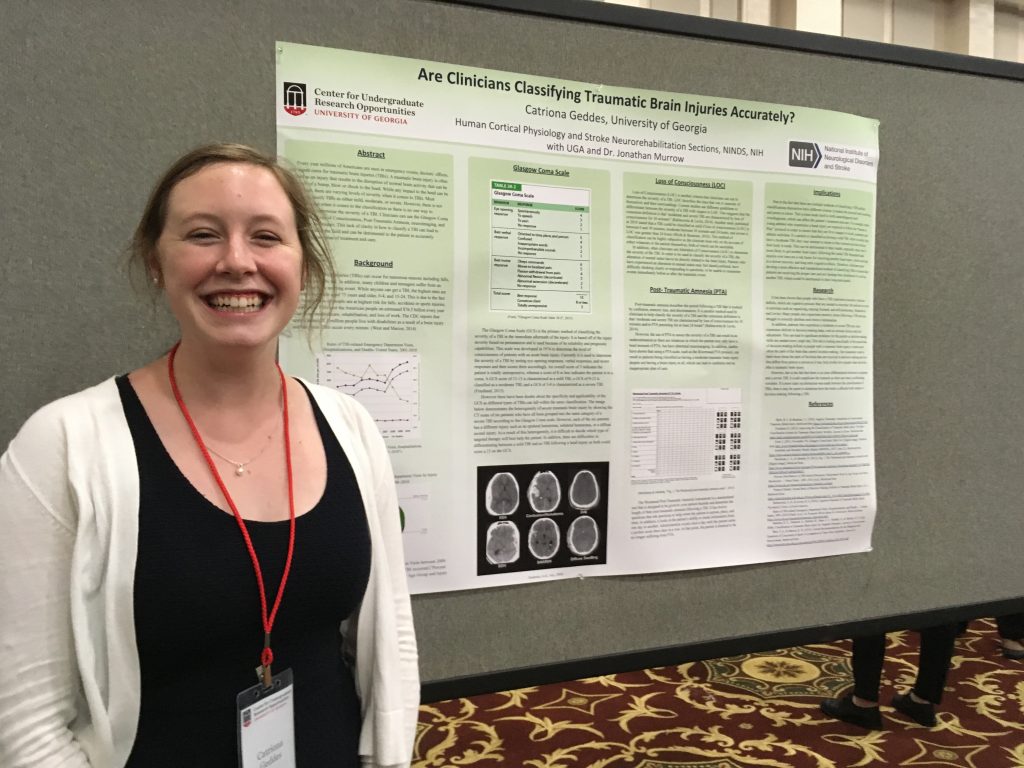

Catriona presented a poster from her summer undergraduate experience at NIH on classifying traumatic brain injuries, as well as an oral presentation on her senior thesis project: Gender Differences in Occupational Physical Activity.
Chantal (left) and Sarah (right) presented sections from a systematic review of the literature on ability to climb stairs and mental well-being. They have been working all year on the systematic review with Dr. Gay and Dr. O’Connor (UGA-Kinesiology). A manuscript from this project was recently submitted for peer-reviewed publication.
Congratulations to all of you on your research successes!


