A Start

Oceans cover the Earth’s surface and house amazing mysteries that humans have just scraped the top of. The sea is nearly undiscovered from deep undiscovered creatures to the newly found Antarctic exploration ship, the “Endurance” found in near-mint condition (compared to other shipwrecks). Incredible innovations in the digital age pertain to ocean exploration, ocean preservation, and other ocean topics. Today we will focus on pirates and illegal ships and more importantly innovations on how to catch and track them.
This blog will be split into two parts. Part one will be focused on pirates and their effect on trade and government, along with illegal fishing and the effect on fish populations and aquatic ecosystems. Part two will focus on the digital innovation part with satellite and radio frequency (RF) tracking for undocumented boats, which help track boats and lead to the top of captains on the high seas endangering our world trade and oceans as we know them today.

The ocean is home to an estimated 20,000 species of fish that have been discovered today, and most likely many more that researchers haven’t found. The Oceans support trade and provide the greatest percentage of protein for human consumption, and according to savethesea.org, “More than 3.5 billion people depend on the ocean for their primary source of food. In 20 years, this number could double to 7 billion.” 195 ships were attacked by pirates in 2020, and 132 in 2021, and the number seems to be trending down due to increase awareness of cargo vessels and increase the security of these vessels.
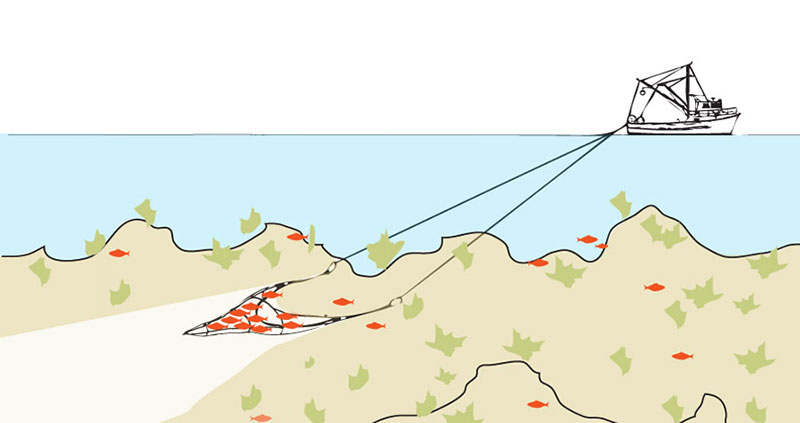

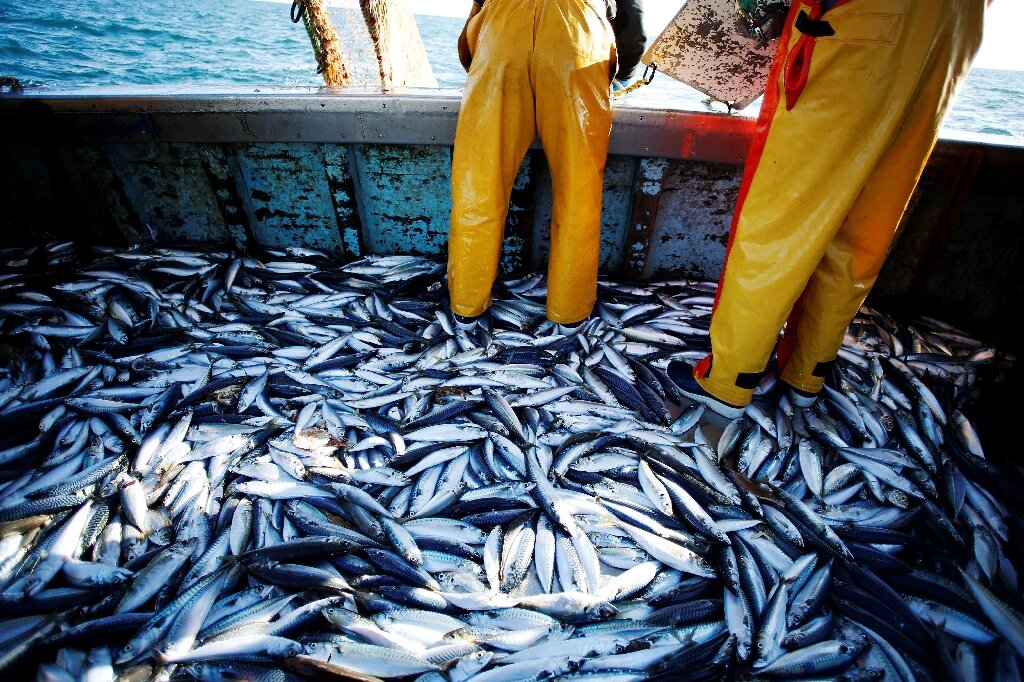
Overfishing is a prevalent issue in many coastal communities and especially lower GDP economies where many civilians rely on fishing for food and a living. Depletion of fish populations can lead to a chain effect of die out for certain fish populations being targeted, loss of prey for predators in the environment, habitat destruction from trolling (a technique of fishing with a net as shown in the photo above), and also economic impact for fishing communities with a die out of fish as their main source of income and food. With the threat of overfishing, governments (for example the United States Department of Natural Resources) have: enacted fishing quotas to limit the amount of fish you can take out of the ecosystem, promoted sustainable fishing practices such as large mesh nets, reduced subsidies for fishing industries, and take advantage of boat tracking systems to deter overfishing violations. All of these efforts have two things in common: boats need to be registered, and captains need to follow the laws. In the second part of this post, we will see how fishermen get around these laws and how startups, government systems, and other organizations have leveraged technology to bring these practices to a halt.

Piracy on the high seas is not the same as we see on screen as Jack Sparrow escapes from the chains of the British and plunders unsuspecting galleons by the tip of his sword. While Jack Sparrow-like tales were once true, modern pirates have a more sleek approach when it comes to hijacking large cargo vessels by using small boats, makeshift ladders, and weapons to subdue the crew and take the ship.
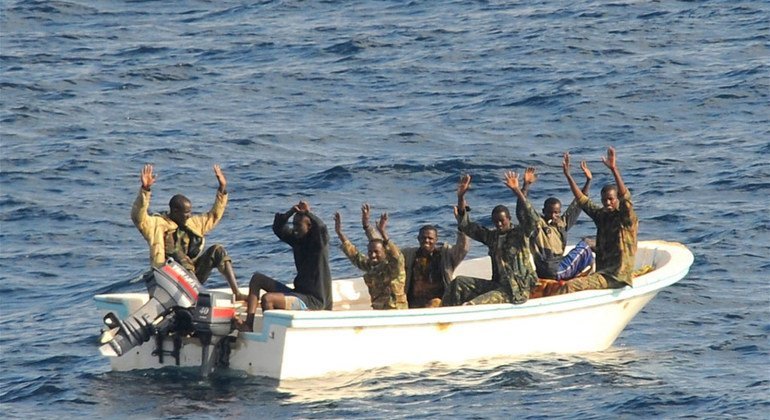

While Numbers have been dropping in recent years maritime piracy, the number still stands at 115 incidences in 2022, 132 in 2021, and 195 in 2020. In a study from 2011 to 2012, “For every $120 million seized by pirates in Somalia, the cost to the shipping industry and the end consumer is between $0.9 and $3.3 billion.” While these numbers are outdated, you can see the impact of products seized by pirates on the actual cost to the industries and end consumers.
What is being done?
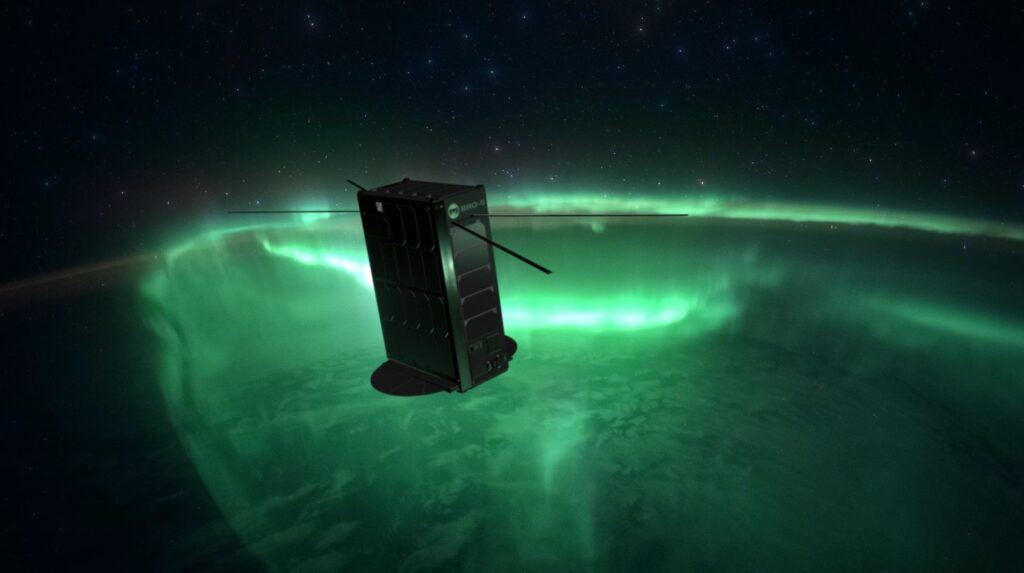

Automatic identification system (AIS) is used in maritime environments for tracking ships usually in the medium to extra large categories (think commercial boats like shrimp boats to cargo vessels). The use of AIS helps regulators track boat usage and whereabouts to prevent violations of policies, quotas, and laws that are in place in maritime environments.
The downside to the AIS is illegally registered vessels or unregistered vessels out on the waters. The lack of a track system in the boat completely disregards the authority’s ability to track and enforce the vessel. The technology called VMS or Vessel Monitoring systems has been active for a while using GPS to track boats like the AIS systems, just mostly used for government regulatory agencies or fishing industries. Again boats would have a tracker installed on the boat and GPS would be used to track the position and speed of boats, often used to avoid collisions at sea.
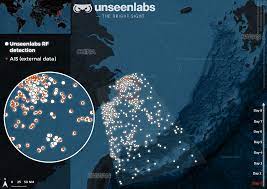
Companies like Unseen- labs, Fleetmon, and many others are using satellites and radio frequencies to locate and track vessel whereabouts out at sea. With satellite and RF data, these companies can find and locate registered and unregistered boats anywhere in the ocean. With the ability to track boats registered or not, they can provide advanced analytics and data to regulatory bodies. With advanced tracking, regulators can find likely attacks on vessels, pirates on the ocean, fishing companies overfishing an area or breaking rules in the industry, blocked shipping lanes, and even use the technology to find shipwrecks and save lives of those on board with advanced sighting technology.
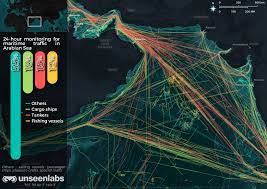
With the ability to track and monitor fishing vessels in real-time, it allows authorities to monitor activity in areas that were previously difficult to monitor like the open ocean or secluded waters away from highly used waterways. This data can be used to stop illegal fishing where fish populations are being caught faster than they can reproduce which will lead to an eventual die-off of the species in that area. Along with tracking vessels the satellites can also track sea temperature and sea color to find phytoplankton populations that are needed for the food chain in the ecosystem.
Although the technology right now is mainly being used for regulation in boating industries like transport and fishing, there are many possible usages of the RF and satellite technology to provide analytics and data to whoever needs them to make the oceans a safer place for trade from piracy and shipping collisions. Along with the benefits of boat tracking for trade, fishermen can also be tracked by all governments and fishery management organizations. The environment is morally ours to protect as we continue to develop our world, and as we develop, technology is becoming increasingly useful for protecting the Earth we were given.
Lastly I wanted to mention some other maritime innovations that were cool to come across in my research of this subject. Along with satilities and their usefulness in many areas of marinetime trade and conservation, there are also: artificial reefs, remote sensing technology, smart bouys, wave powered generators, floating wind turbines, and many others. Smart buoys are tracking wave height along with water temperate and ocean swells to provide data that can be used to monitor ecosystems in the ocean and even warn against incoming floods, tsunamis, and environmental hazards. Wave powered electric generators are providing a new sustainable energy option to replace fossil fuels or at least cut back on fossil fuel consumption. Remote sensors can help track animal migration, environmental changes, oil spills, marine life distribution, and many other things. The effect of technology will forever help improve out oceans and the land of the Earth, if we continue to innovate and use technology for good.
Thank you for reading my blog post!
Sources
Addressable markets. UNSEENLABS. (2021, January 7). Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://unseenlabs.space/use-cases/
Akan, E., Gültekin, T., & Bayar, S. (2022, August 3). Statistical analysis of maritime piracy cases in World Territorial Waters – Journal of Transportation Security. SpringerLink. Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12198-022-00251-z
Interesting Ocean Facts. Ocean facts. (n.d.). Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://savethesea.org/STS%20ocean_facts.htm
Long, T. (2015, November 20). Satellite tracking can unmask illegal fishing vessels. The Pew Charitable Trusts. Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://www.pewtrusts.org/en/research-and-analysis/articles/2015/11/20/satellite-tracking-can-unmask-illegal-fishing-vessels
News. SatNews. (2022, December 22). Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://news.satnews.com/2022/12/22/frances-unseenlabs-8th-space-based-rf-detection-satellite-specific-to-maritime-surveillance-is-ready-to-launch/
Placek, M. (2022, July 27). Number of pirate attacks worldwide. Statista. Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/266292/number-of-pirate-attacks-worldwide-since-2006/
Researchers Tim Besley , Researchers, & Tim Besley Professor of Economics and Political Science. (2011, October 1). The economic costs of piracy. International Growth Centre. Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://www.theigc.org/collections/economic-costs-piracy
Satellite AIS – space-based vessel tracking. FleetMon.com. (n.d.). Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://www.fleetmon.com/services/satellite-ais/
Staff, N. N. (2022, March 31). Unseenlabs to launch two more satellites dedicated to ship geolocation. Naval News. Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://www.navalnews.com/naval-news/2022/03/unseenlabs-to-launch-two-more-satellites-dedicated-to-ship-geolocation/
What to do about piracy? United Nations : Office on Drugs and Crime. (n.d.). Retrieved February 20, 2023, from https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/frontpage/what-to-do-about-piracy-.html